ENS Names
Farcaster uses ENS names as human readable identifiers for accounts. Two kinds of ENS names are supported:
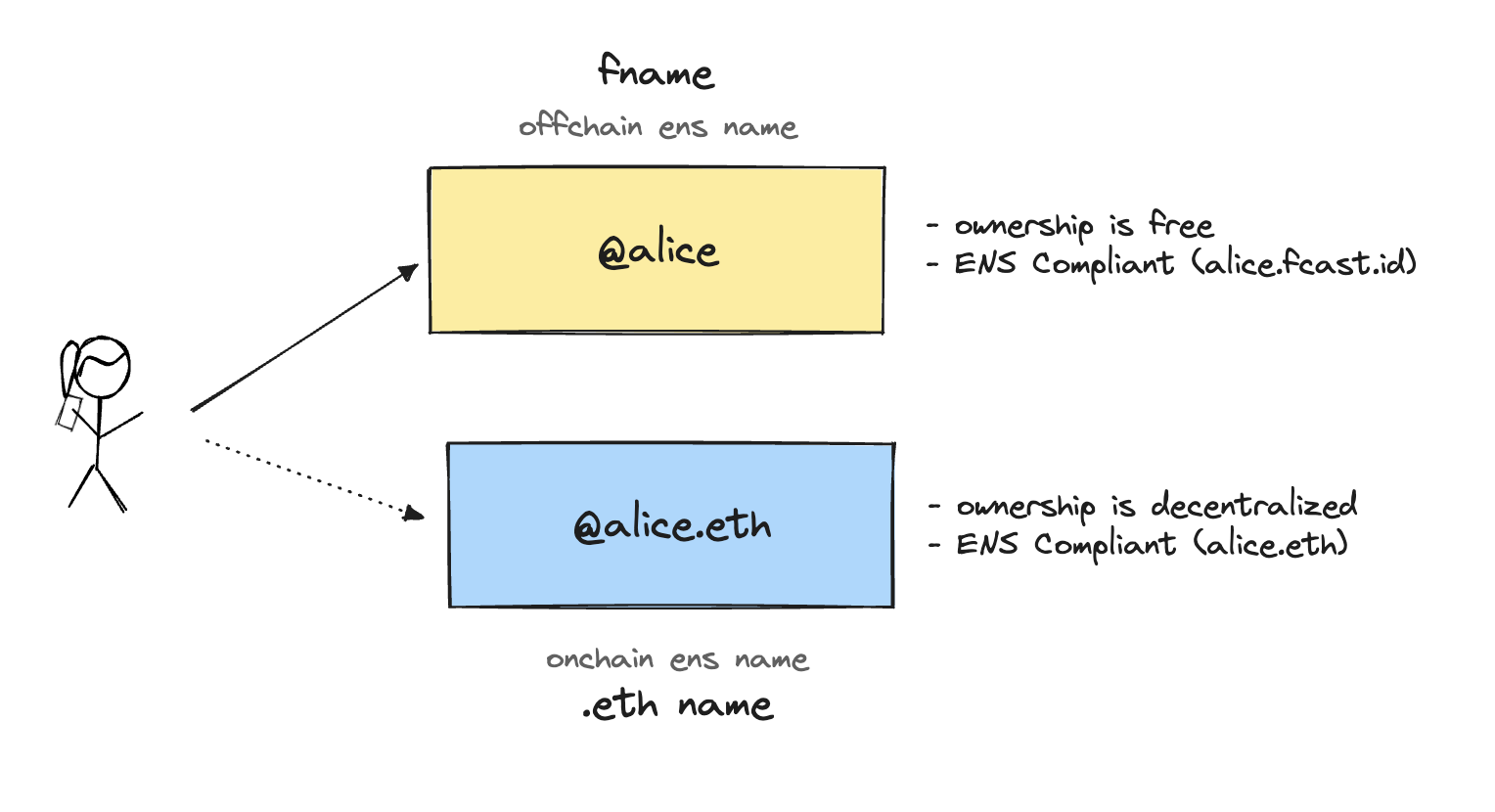
- Offchain ENS names: free and controlled by farcaster. (e.g. @alice)
- Onchain ENS names: costs money and is controlled by your wallet. (e.g. @alice.eth)
ENS names can only be used on Farcaster if they are <= 16 characters and contain only lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens.
Onchain ENS Names
Users can use onchain ENS names like @alice.eth on Farcaster.
Onchain ENS names are issued by ENS, end in .eth and must be registered on the Ethereum L1 blockchain. Anyone can register an ENS name by using the ENS app.
Users must pay a fee to register an onchain ENS name, but once registered, it is controlled by the user and cannot be revoked.
Offchain ENS Names (Fnames)
Users can use offchain ENS names like @alice on Farcaster.
Offchain ENS names, also called Farcaster Names or Fnames, are compliant with ENS but registered offchain. Fnames are free but are subject to a usage policy to prevent squatting and impersonation. They are also subject to the following requirements:
- An account can only have one Fname at a time.
- An account can change its Fname once every 28 days.
Usage Policy
Registering an Fname is free but subject to the following policy:
- Names connected to public figures or entities may be reclaimed (e.g. @google).
- Names that haven't been used for 60+ days may be reclaimed.
- Names that are registered for the sole purpose of resale may be reclaimed.
Decisions are made by the Farcaster team and often require human judgment. Users who want a name that is fully under their control should use an onchain ENS name.
Registry
Fnames are issued as offchain names under the subdomain fcast.id.
Bob can register the offchain ENS name bob.fcast.id and use it on any Farcaster app with the shorthand @bob. The name can be registered by making a signed request to the Fname Registry server. See the FName API reference for more details on how to query and create Fnames.
To learn more about how Fnames work, see ENSIP-16 and ERC-3668.